

Article tag: Infant catheterization model| Medical catheterization model| BIX-F65|
Pediatric catheterization model has shown its great potential in medical training, and can effectively make up for the shortcomings of traditional training methods. By providing a highly simulated operating experience, increasing opportunities for repetition, simulating high-pressure situations, and providing immediate feedback, it significantly improves ...
In medical training, urinary catheterization technology is one of the basic skills that every medical worker must master. For adult patients, the catheterization operation is relatively simple, but for pediatric patients, due to the particularity of its anatomical structure and physiological characteristics, the catheterization operation is often more difficult and challenging. In order to ensure that medical staff are proficient in this skill, traditional teaching methods often include theoretical study, viewing demonstrations, and a small amount of clinical practice. However, these traditional methods have certain limitations when dealing with pediatric patients. In order to solve these problems, pediatric catheterization training model came into being, and gradually became an important tool in medical training. So, can the pediatric catheterization model effectively improve the shortcomings of traditional training methods? This paper will discuss the aspects of medical training, clinical application and data support.
Limitations of traditional training methods
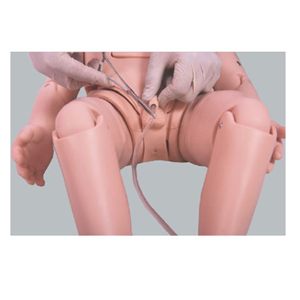
Traditional catheterization training often relies on book learning and clinical practice. Although this approach can help students understand the theoretical basis, in practice, they often face the following problems:
1. Lack of practical operation opportunities
For beginners, traditional training methods often give students the opportunity to do hands-on work during clinical practice. In a busy clinical environment, it is difficult for students to get enough operational opportunities, which may lead to poor mastery of skills.
2. The operation is not accurate enough
Due to the special anatomical structure of children, catheterization is more complicated in children than in adults. The demonstration procedure in traditional methods is mostly for adult patients, and the trainees are unable to grasp the anatomical differences and special needs of pediatric patients in practice.
3. The clinical environment is stressful
In the actual clinical environment, first aid and emergency often put the medical staff in a high pressure state. For a novice, this kind of pressure can easily lead to operational errors. However, traditional training methods lack simulation training, which makes it difficult for students to master the technology in a risk-free environment.
4. Limited training time
The clinical practice time is limited, and students may only be able to perform urinary catheterization training in a short period of time, which makes the learning process lack of enough repetitive exercises, and it is difficult to ensure the operation accuracy of students and the ability to respond to emergency situations.
Advantages of urinary catheterization model in children
With the development of simulated medical education, pediatric catheterization model, as an innovative training tool, has been widely used in medical training. These models are not only highly simulated and can simulate the anatomical characteristics of pediatric patients, but also provide real-time feedback and diverse training scenarios, helping to compensate for the shortcomings of traditional training methods.
1. Anatomical structure with high degree of imitation
The infantile catheterization model accurately simulates the urethra, bladder and surrounding tissue structure of pediatric patients to provide a more realistic clinical experience. In the absence of real patients, students can fully master the precise methods of pediatric catheterization, including how to determine the position of the urethral opening, how to insert the catheter, and how to avoid accidental injury during the operation.
2. Repeat practice opportunities
Pediatric catheterization models can provide repeated operation opportunities to help participants gain experience in a simulated environment. For beginners, this repeated training opportunity is very valuable, helping them to better master the catheterization skills, improve the proficiency and accuracy of the operation.
3. A risk-free high-pressure training environment
In clinical practice, healthcare professionals can be stressed out when dealing with pediatric patients, especially in emergency situations. The pediatric catheterization model can simulate these high-pressure situations, so that students can practice in an environment without actual risks, and gradually improve their ability to cope with stress, thus laying the foundation for future clinical work.
4. Real-time feedback and evaluation
Many pediatric catheterization models are equipped with real-time feedback systems that provide immediate assessment based on the student's actions. For example, if the position of the intubation tube is not accurate, the model may remind the student to adjust it through visual or sound signals. This feedback mechanism can help students quickly find and correct the shortcomings in operation, and improve the efficiency of skill learning.
5. Diversified clinical scenario simulation
The infantile catheterization model is not only suitable for the training of routine operations, but also can simulate different clinical situations, such as urethral stenosis and inflammation of the urethral opening, which are difficult to cover in traditional training. By simulating these complex scenarios, students are able to better understand and respond to catheterization operations in different pathological situations.
Data support and practical effects
The study showed that the operation skills and emergency response ability of medical staff were significantly improved by using the pediatric catheterization training model. According to a study of medical students, after training with a pediatric catheterization model, the success rate of the trainees in the actual operation was about 25% higher than that of the trainees who did not use the model. In addition, about 85% of participants who received model training said that training with the model gave them a better understanding of clinical operations and increased their confidence in operating in high-pressure situations.
Case study
In the pediatric practice course of a medical school, the students first carried out a series of simulation training through the pediatric urinary catheterization model before the operation of pediatric urinary catheterization. The results showed that these students showed a clear advantage in clinical practice. In an emergency situation, a student quickly completed the catheterization procedure in the clinic, and the procedure was smooth and smooth. Later, the student recalled: "In the simulation training, I have faced similar emergency situations many times, through the repeated practice of the model, I became more skilled, but also more calm to deal with the actual operation."
conclusion
Pediatric catheterization model has shown its great potential in medical training, and can effectively make up for the shortcomings of traditional training methods. By providing a highly simulated operating experience, increasing opportunities for repetition, simulating high-pressure situations, and providing immediate feedback, it significantly improves the operational accuracy, skill level, and ability to respond to emergency situations. In the future, with the adoption of more medical institutions and education platforms, catheterization models will play an increasingly important role in the training of medical personnel and become an indispensable part of medical education.