

Article tag: Parenteral nutrition nursing model| medical nursing model|
In medical education and clinical practice, the model of parenteral nutrition care plays a crucial role. It not only provides a platform for students and medical staff to simulate the real environment, but also makes the operation training more vivid, intuitive and efficient...
In medical education and clinical practice, the model of parenteral nutrition care plays a crucial role. It not only provides a platform for students and medical staff to simulate the real environment, but also makes the operation training more vivid, intuitive and efficient through accurate simulation.
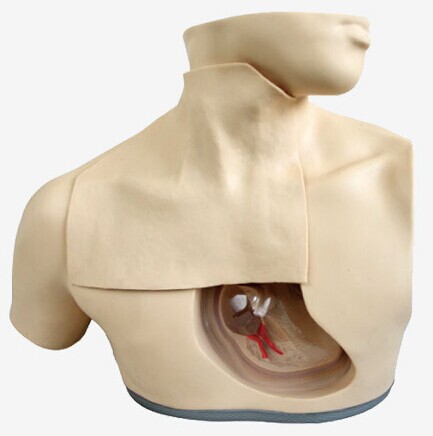
The parenteral nutrition nursing model, as an advanced nursing teaching tool, is designed to strictly follow the principles of human anatomy and physiology. The model usually simulates the body size and anatomy of a normal adult male, including the neck, chest, and internal blood vessels, heart, and part of the lungs. This design allows users to clearly observe the complex structure inside the human body, providing an intuitive basis for in-depth learning and understanding of parenteral nutrition care.
On the model, key vascular structures such as the internal jugular vein and subclavian vein can be clearly seen. These blood vessels are a key channel for parenteral nutrition therapy, through which patients can be provided with necessary nutritional support. Therefore, the training of central vein catheterization, disinfection, puncture and fixation on the model is very important to improve students' operation skills and clinical practice ability.
The precise simulation characteristics of the parenteral nutrition nursing model make the operation training more real and effective. The simulated puncture holes, blood vessels and heart structures on the model are highly similar to real human structures. This enables the students to be closer to the actual clinical operating environment and improve the pertinence and practicability of the training.
In addition, the parenteral nutrition nursing model also has the characteristics of transparent design. This design allows the user to clearly observe the bone, blood vessel and heart structure inside the model, further enhancing the intuitiveness and operability of the model. Through transparent design, students can gain a deeper understanding of the anatomy and physiological functions inside the human body, laying a solid foundation for future clinical practice.
In conclusion, accurately simulated parenteral nutrition care models provide important support for medical education and clinical practice. Through the operation training of this model, students' operation skills and clinical practice ability can be improved, and more outstanding talents can be cultivated for the future medical career.